
Biomass boilers are increasingly becoming a popular choice for heating and industrial processes, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuel-based systems. Understanding the daily fuel consumption of biomass boilers is essential for efficient operation, cost management, and environmental sustainability. This article delves into the factors that affect biomass boiler fuel consumption, calculation methods, and examples for different scenarios.
What is a biomass boiler?
1. Definition and working principle of biomass boiler
A biomass boiler is a boiler device that converts biomass fuel into thermal energy, which can provide hot water or steam for industrial and civil scenarios. Its working principle is to heat water or generate steam by burning biomass fuel to generate high temperature. Specifically, a biomass boiler burns biomass fuel in a combustion chamber, and the heat generated by the combustion heats the water to the required temperature or pressure through a heat transfer system. Boilers are usually equipped with a fuel delivery system, an automatic control system, and a smoke treatment device to ensure stable, safe, and efficient operation of the boiler.
The advantages of biomass boilers are renewability and environmental protection. Compared with traditional coal-fired boilers, biomass boilers have lower carbon dioxide emissions and a wide range of fuel sources, which can effectively reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources.

2. Types and characteristics of biomass fuels
Common fuels for biomass boilers include sawdust, biomass pellets, and crop waste. These fuels have their own characteristics and provide flexible choices for different application scenarios.
Sawdust: Sawdust is usually a byproduct of wood processing, sawmills or furniture factories. It has good flammability, small fuel particles, and is easy to burn and transport. The advantage of sawdust fuel is that it has a high combustion calorific value and is suitable for heating, power generation and other purposes, but its water content needs to be controlled to improve combustion efficiency.
Biomass pellets: Biomass pellets are small particle fuels formed by compressing wood chips, sawdust, rice husks, etc. Biomass pellet fuel burns evenly, has a stable calorific value, high density, and is easy to store and transport. It is an efficient and clean fuel that is widely used in heating and industrial boiler systems. It has the advantages of low ash content and low pollution.
Crop waste: Crop waste includes rice straw, corn stalks, wheat straw, etc. This type of fuel is widely available and low cost, but it will produce a certain amount of ash and emissions when burned. The combustion technology of crop waste usually requires specially designed combustion equipment to achieve complete combustion and reduce pollution emissions.

Factors affecting fuel consumption
In the operation of biomass boilers, fuel consumption is a key factor affecting its economy and environmental protection. In order to effectively control fuel consumption, it is necessary to understand the various factors affecting fuel consumption, including the calorific value of fuel and the thermal efficiency of the boiler, ambient temperature and usage, and the impact of fuel humidity on combustion efficiency.
1. Fuel calorific value and boiler thermal efficiency
The calorific value of fuel refers to the heat released by a unit weight of fuel during the combustion process, which is an important factor affecting fuel consumption. Fuels with high calorific value can provide more heat energy with less consumption, thereby improving the combustion efficiency and heat production capacity of the boiler. On the other hand, the thermal efficiency of the boiler determines the proportion of heat that can be truly converted into useful heat energy during the combustion process. Boilers with high thermal efficiency can better utilize the heat released by the fuel, reduce heat loss, and thus reduce fuel consumption. Therefore, selecting fuels with high calorific value and optimizing boiler thermal efficiency can effectively reduce fuel consumption and achieve more economical operation.
2. Ambient temperature and boiler usage
The ambient temperature has a direct impact on boiler fuel consumption. Lower ambient temperatures will cause the boiler to consume more fuel to maintain the set water temperature or steam pressure, especially in cold areas or winter. In addition, the use of the boiler will also affect fuel consumption. Frequent startup and shutdown will lead to energy waste, because each time the boiler starts, additional fuel is needed to heat the boiler body and system, and long-term high-load operation may increase fuel consumption and accelerate equipment wear. Therefore, maintaining reasonable operating time and load management can reduce fuel consumption and improve operating efficiency.

3. Fuel humidity and its impact on combustion efficiency
Fuel humidity is another important factor affecting combustion efficiency. Biomass fuel with high humidity needs to consume more heat to evaporate water during combustion, which will reduce the effective calorific value of the fuel, resulting in a decrease in combustion efficiency, thereby increasing fuel consumption. Wet fuel will not only reduce the calorific value of the boiler, but also cause incomplete combustion, produce more smoke and residue, and increase the maintenance cost of the boiler. Therefore, in order to reduce fuel consumption and improve combustion efficiency, the humidity of the biomass fuel must be reduced as much as possible before use to ensure that it is in a state suitable for combustion. This can be achieved through drying, reasonable storage and selection of suitable combustion equipment.
4. Heat demand
The amount of heat or steam required by the system determines the operating load of the boiler. High demand results in increased fuel usage.
5. Operating hours
A boiler that operates 24 hours a day will naturally consume more fuel than a boiler that operates 8 hours a day.
6. System design
The integration of auxiliary components such as economizers or heat recovery systems can increase overall efficiency and reduce fuel consumption.
Calculating Biomass Boiler Fuel Consumption
To estimate the fuel consumption of a biomass boiler, use the following formula:
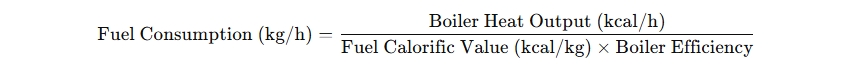
For daily consumption:
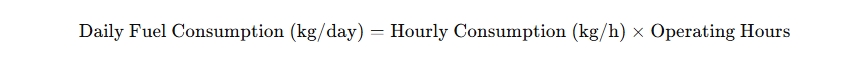
Examples of Biomass Boiler Fuel Consumption
Let’s calculate the fuel consumption for a 10-ton/hour biomass boiler running 24 hours a day with wood pellets as fuel:
- Boiler Specifications:
- Heat Output: 10 tons/hour of steam ≈ 6,000,000 kcal/hour
- Boiler Efficiency: 90%
- Fuel Calorific Value (Wood Pellets): 4,500 kcal/kg
- Hourly Fuel Consumption:
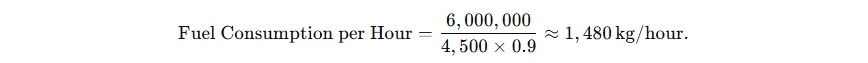
- Daily Fuel Consumption:
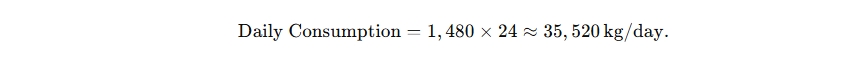
Optimizing Biomass Boiler Fuel Consumption
To minimize fuel consumption and operational costs, consider the following strategies:
Fuel Quality:
Use biomass with low moisture content and high calorific value.
Efficient Boiler Operation:
Regularly clean heat exchange surfaces to maintain efficiency.
Optimize combustion settings for complete fuel burning.
Thermal Storage Systems:
Incorporate thermal storage to smooth out demand fluctuations, reducing peak load operation.
Energy Recovery:
Use economizers and condensers to recover heat from flue gases.
Periodic Maintenance:
Address issues such as clogs, leaks, or worn-out components to maintain optimal performance.

Environmental and Economic Benefits
Carbon Neutrality:
Biomass is considered carbon-neutral since the CO₂ emitted during combustion is offset by the CO₂ absorbed during the growth of biomass sources.
Cost Savings:
In regions where biomass is readily available, it can be a cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels.
Sustainability:
Biomass boilers contribute to reducing dependency on finite resources like coal and oil.
Conclusion
Understanding the fuel consumption of a biomass boiler is essential for cost optimization, efficient operation, and environmental sustainability. Factors like fuel type, quality, boiler efficiency, and operating conditions all influence daily consumption. By selecting high-quality biomass, maintaining boilers regularly, and using advanced technologies, users can minimize fuel use while maximizing the benefits of this renewable energy source.
With the growing emphasis on green energy, biomass boilers represent a practical and sustainable solution for heating and industrial processes.
Get your best price
Quickly compare 3 FREE quotes
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
25 years+ of boiler R&D
More than 20 innovative technologies
PRODUCT
-
Gas Boilers
-
Oil Boilers
-
Electric Boilers
-
Coal Boilers
-
Biomass Boilers
-
Industrial Boilers

